Partial Criteria
The figure shows the dialog box which allows to select optimization parameters. It also allows to select or enter values for the additional parameters (weight and normalizing values) which determine their participation in the global criterion. You can choose a set of criteria, weights and values normalizing particular partial criteria. To select the given criterion, use the appropriate button in the column Set.
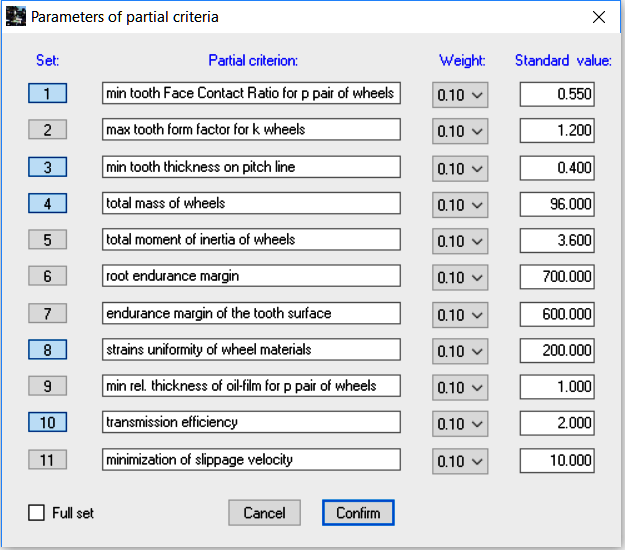
Clicking the Full set check box selects the full set option.
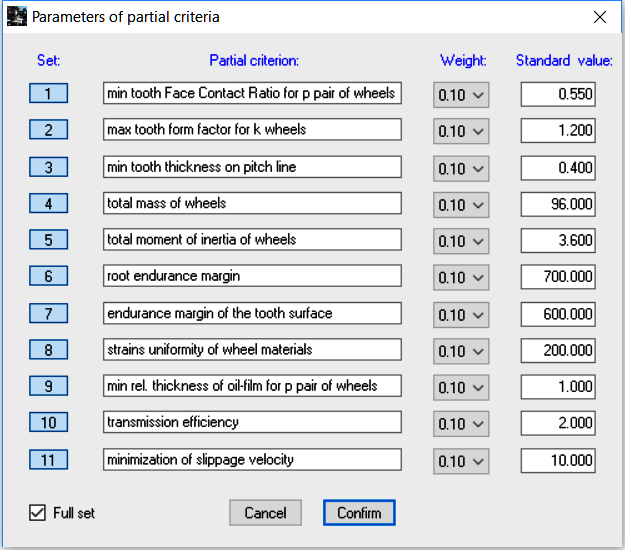
The weights of particular criteria should be chosen such that for the given set of criteria, their sum should total '1'. For identical weight coefficients in the given set, normalised values should ensure the similar contribution of particular partial criteria to the value of the global criterion.
Partial criteria can be combined with one another in any way. When a given partial criterion is not selected from the set, its weight coefficient is zeroed during the calculation procedure, no matter what its current value in the window 'Parameters of partial criteria'. A set of partial criteria can be modified and extended, depending on the users’ needs.
Clicking Cancel returns you to the Status of the Project dialog window. The modified data concerning partial criteria are not approved in this case. Clicking Confirm approves the set of criteria along with their parameters and returns you to the Status of the Project dialog window.
Partial criteria can be divided into 4 groups:
- geometric criteria (K1 , K2 , K3),
- mass criteria (K4 , K5),
- strength criteria (K6 , K7 , K8),
- operation criteria (K9,K10,K11).
Selected partial criteria have been determined, as shown below:
- an inverse of minimal tooth face contact ratio εα for a ‘p’ pair of wheels:
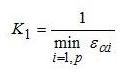
- a maximal tooth form factor yF for ‘k’ wheels:
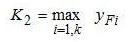
- an inverse of the absolute value of minimal tooth thickness at peak Sα for ‘k’ wheels:
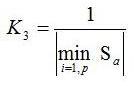
- total mass of wheels:
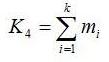
- total moment of inertia of wheels:
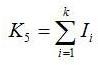
- root endurance margin:
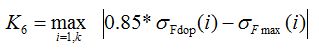
where: σFdop - allowable fatigue strength of the tooth root
σFmax - maximal stress of the tooth root
- endurance margin of the tooth surface:
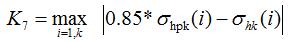
where: σhpk - allowable stress of the tooth side
σhk - calculation stress of the tooth side
- strains uniformity of wheel materials:
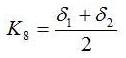
where: σ1 - standard deviation of the difference 0.85*σFdop - σFmax
σ2 - standard deviation of the difference 0.85*σhpk - σhk
- minimal relative thickness of oil-film for the ‘p’ pair of wheels:
A minimal relative (related to roughness parameter Ra) thickness of the lubricant layer λj is calculated for 5 characteristic points of the toothed pair. Subsequently, substitute thickness of the lubricant layer λz, measured with weights uj:
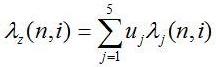
n - gear number, n=1,b
i - toothed pair number, i=1,p
K9 criterion is expressed with the equation:
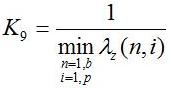
and the global criterion was written with the dependance:
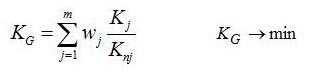
where:
|
b |
- |
number of gear speeds, |
|
p |
- |
number of wheel pairs, |
|
k |
- |
number of wheels, |
|
no |
- |
index of not meeting constraints , ‘no’ takes value 0 or 1, |
|
lo |
- |
number of functional constraints (equality and inequality), |
|
m |
- |
number of criteria, |
|
wj |
- |
weight coefficient of ‘j’ partial criterion, |
|
Knj |
- |
value standardizing ‘j’ partial criterion. |